Durham University가 이끄는 천문학자들은 DiRAC HPC 시설에서 중력 렌즈 효과와 슈퍼컴퓨터 시뮬레이션을 사용하여 태양의 300억 배 이상의 질량을 가진 지금까지 발견된 가장 큰 블랙홀 중 하나를 발견했습니다. 우주를 통과하는 빛을 시뮬레이션하는 이 획기적인 기술을 통해 연구자들은 실제 허블 우주 망원경 이미지에서 볼 수 있는 빛의 경로를 정확하게 예측할 수 있었습니다. 이 발견은 왕립천문학회 월간 공지.
천문학자 팀이 중력 렌즈 현상이라는 현상을 이용하여 지금까지 발견된 가장 큰 블랙홀 중 하나를 발견했습니다.
빛의 곡선 중력
영국 더럼 대학이 이끄는 팀은 전경 은하가 멀리 있는 물체의 빛을 휘게 하고 확대하는 중력 렌즈 효과를 사용했으며, DiRAC HPC 시설에서 슈퍼컴퓨터 시뮬레이션을 통해 빛이 블랙홀에 의해 어떻게 휘어지는지 면밀히 조사할 수 있었습니다. 수백 마일 떨어진 은하계 내부 지구에서 수백만 광년.
팀은 우주를 수십만 번 이동하는 빛을 시뮬레이션했으며 각 시뮬레이션에는 서로 다른 질량이 포함되었습니다.[{” attribute=””>black hole, changing light’s journey to Earth.

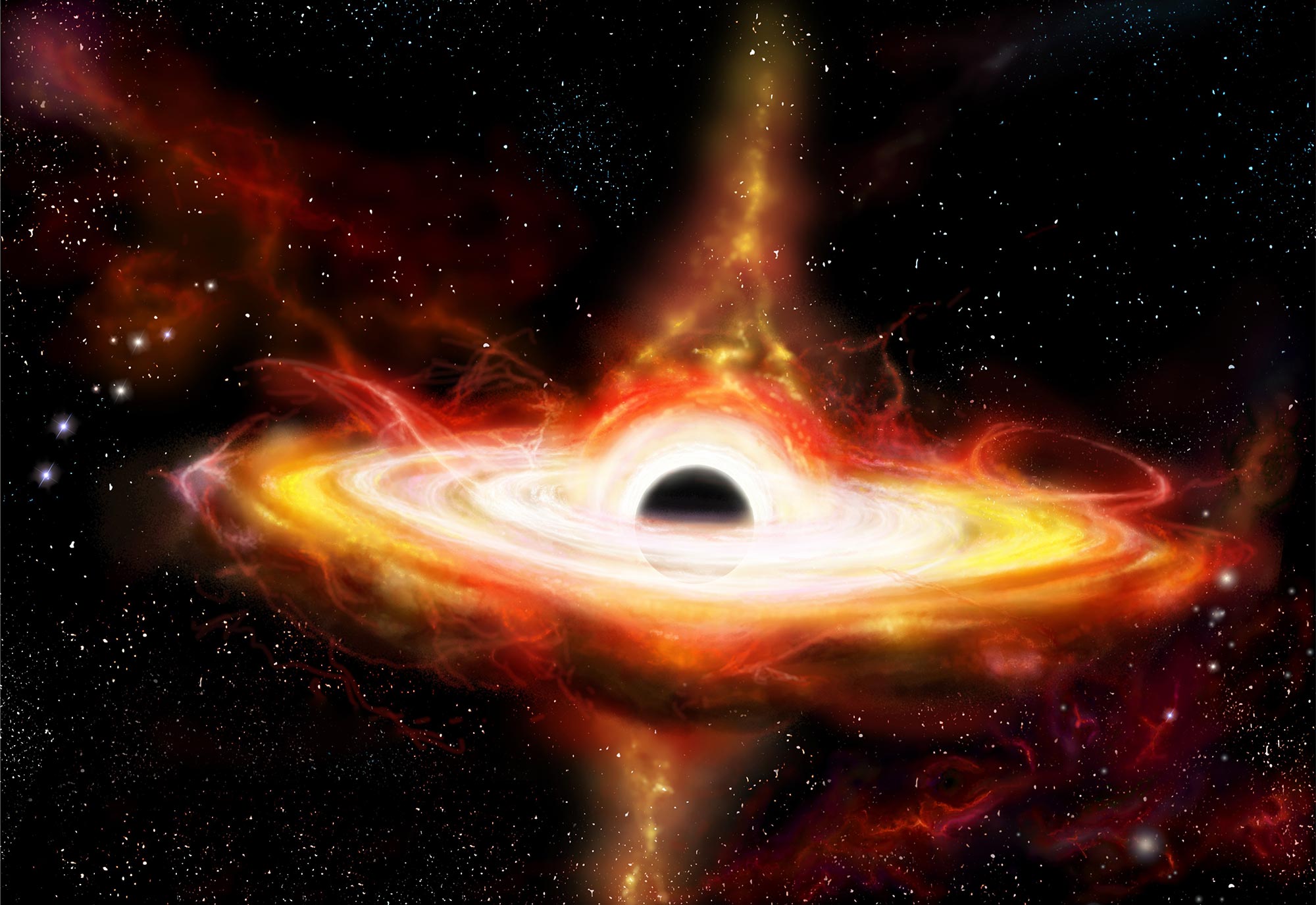
An artist’s impression of a black hole, where the black hole’s intense gravitational field distorts the space around it. This warps images of background light, lined up almost directly behind it, into distinct circular rings. This gravitational “lensing” effect offers an observation method to infer the presence of black holes and measure their mass, based on how significant the light bending is. The Hubble Space Telescope targets distant galaxies whose light passes very close to the centers of intervening fore-ground galaxies, which are expected to host supermassive black holes over a billion times the mass of the sun. Credit: ESA/Hubble, Digitized Sky Survey, Nick Risinger (skysurvey.org), N. Bartmann
30 billion times the mass of our Sun
When the researchers included an ultramassive black hole in one of their simulations, the path taken by the light from the faraway galaxy to reach Earth matched the path seen in real images captured by the Hubble Space Telescope.
What the team had found was an ultramassive black hole, an object over 30 billion times the mass of our Sun, in the foreground galaxy – a scale rarely seen by astronomers.
This is the first black hole found using gravitational lensing and the findings were published today (March 29) in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
천문학자들이 20억 광년 떨어진 은하에서 태양 질량의 300억 배에 달하는 블랙홀을 발견하기 위해 중력렌즈를 사용한 방법을 보여주는 비디오. 크레딧: 더럼 대학교
우주의 시간을 되돌아보며
우리가 알고 있는 가장 큰 블랙홀의 대부분은 활성 상태에 있습니다. 블랙홀 근처로 끌어당겨지는 물질이 가열되고 빛, X선 및 기타 방사선의 형태로 에너지를 방출하기 때문입니다.
중력 렌즈 효과를 통해 비활성 블랙홀을 연구할 수 있는데, 이는 현재 먼 은하계에서는 불가능합니다. 이 접근 방식을 통해 천문학자들은 이전에 생각했던 것보다 더 큰 비활성 블랙홀을 감지하고 어떻게 그렇게 거대해지는지 조사할 수 있습니다.
바로 이 발견의 이야기는 2004년 더럼 대학의 동료 천문학자인 Alastair Edge 교수가 SGS 이미지를 검토할 때 중력 렌즈의 거대한 호를 발견하면서 시작되었습니다.
19년을 빨리 감고[{” attribute=””>NASA’s Hubble telescope and the DiRAC COSMA8 supercomputer facilities at Durham University, Dr. Nightingale and his team were able to revisit this and explore it further.
Exploring the mysteries of black holes
The team hopes that this is the first step in enabling a deeper exploration of the mysteries of black holes, and that future large-scale telescopes will help astronomers study even more distant black holes to learn more about their size and scale.
Reference: “Abell 1201: detection of an ultramassive black hole in a strong gravitational lens” by J W Nightingale, Russell J Smith, Qiuhan He, Conor M O’Riordan, Jacob A Kegerreis, Aristeidis Amvrosiadis, Alastair C Edge, Amy Etherington, Richard G Hayes, Ash Kelly, John R Lucey and Richard J Massey, 29 March 2023, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad587
The research was supported by the UK Space Agency, the Royal Society, the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC), part of UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), and the European Research Council.
This work used both the DiRAC Data Intensive Service (CSD3) and the DiRAC Memory Intensive Service (COSMA8), hosted by University of Cambridge and Durham University on behalf of the DiRAC High-Performance Computing facility.

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”