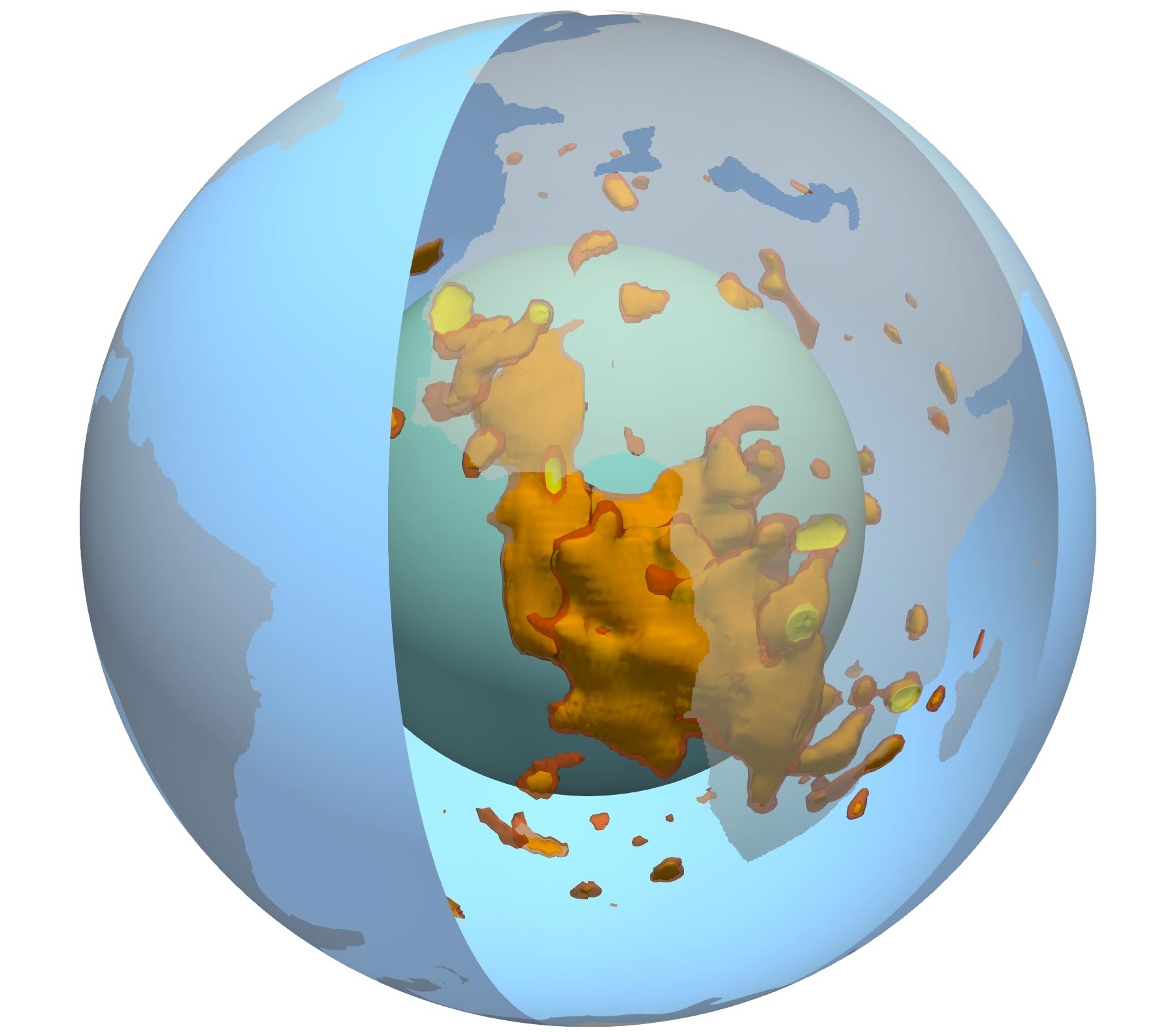
빨간색, 노란색 및 주황색으로 표시된 아프리카 아래의 지구 맨틀 지점의 3D 보기. 청록색은 주요 맨틀 경계를 나타내고 파란색은 표면을 나타내며 투명한 회색은 대륙을 나타냅니다. 크레딧: Mingming Li / ASU
지구는 얇은 외부 지각, 두껍고 끈적끈적한 맨틀, 액체 외부 핵 및 단단한 내부 핵으로 구성된 양파처럼 층을 이루고 있습니다. 맨틀 내부에는 대략 행성의 양쪽에 두 개의 거대한 점 같은 구조가 있습니다. 공식적으로 LLSVP(Large Low Speed Provinces)라고 하는 이 지점은 각각 대륙 크기이며 에베레스트 산보다 100배 높습니다. 하나는 아프리카 대륙 아래에 있고 다른 하나는 태평양 아래에 있습니다.
과학자들은 지진파를 측정하는 장비를 사용하여 이 두 개의 덩어리가 복잡한 모양과 구조를 가지고 있다는 것을 알고 있지만 주목할만한 특징에도 불구하고 덩어리가 존재하는 이유나 이상한 모양을 초래한 원인에 대해서는 알려진 바가 거의 없습니다.
ASU 과학자 Qian Yuan과 Mingming Li of Earth and Space Exploration 대학은 발표된 지진 연구의 지구역학적 모델링과 분석을 사용하여 이 두 지점에 대해 자세히 알아보기 시작했습니다. 그들의 연구를 통해 그들은 얼룩이 도달하는 최대 높이와 맨틀의 주변 점도뿐만 아니라 얼룩의 크기와 밀도가 높이를 제어할 수 있는 방법을 결정할 수 있었습니다. 그들의 연구는 최근에
The results of their seismic analysis led to a surprising discovery that the blob under the African continent is about 621 miles (1,000 km) higher than the blob under the Pacific Ocean. According to Yuan and Li, the best explanation for the vast height difference between the two is that the blob under the African continent is less dense (and therefore less stable) than the one under the Pacific Ocean.
To conduct their research, Yuan and Li designed and ran hundreds of mantle convection models simulations. They exhaustively tested the effects of key factors that may affect the height of the blobs, including the volume of the blobs and the contrasts of density and viscosity of the blobs compared with their surroundings. They found that to explain the large differences of height between the two blobs, the one under the African continent must be of a lower density than that of the blob under the Pacific Ocean, indicating that the two may have different composition and evolution.
“Our calculations found that the initial volume of the blobs does not affect their height,” lead author Yuan said. “The height of the blobs is mostly controlled by how dense they are and the viscosity of the surrounding mantle.”
“The Africa LLVP may have been rising in recent geological time,” co-author Li added. “This may explain the elevating surface topography and intense volcanism in eastern Africa.”
These findings may fundamentally change the way scientists think about the deep mantle processes and how they can affect the surface of the Earth. The unstable nature of the blob under the African continent, for example, may be related to continental changes in topography, gravity, surface volcanism and plate motion.
“Our combination of the analysis of seismic results and the geodynamic modeling provides new insights on the nature of the Earth’s largest structures in the deep interior and their interaction with the surrounding mantle,” Yuan said. “This work has far-reaching implications for scientists trying to understand the present-day status and the evolution of the deep mantle structure, and the nature of mantle convection.”
Reference: “Instability of the African large low-shear-wave-velocity province due to its low intrinsic density” by Qian Yuan and Mingming Li, 10 March 2022, Nature Geoscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41561-022-00908-3

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”