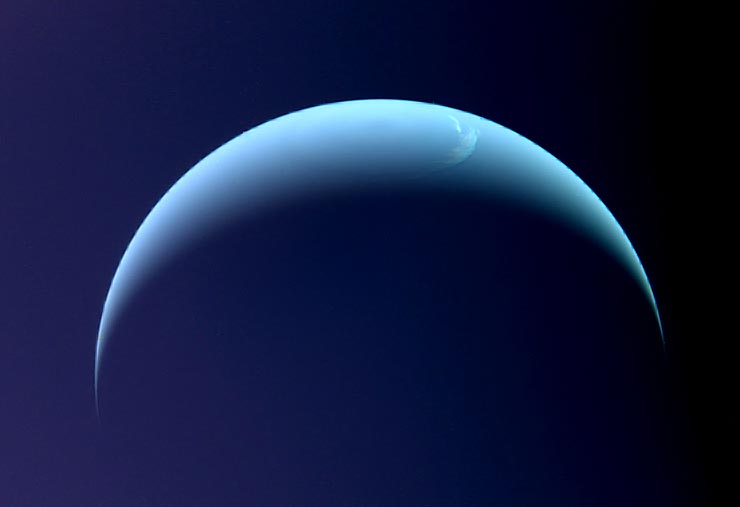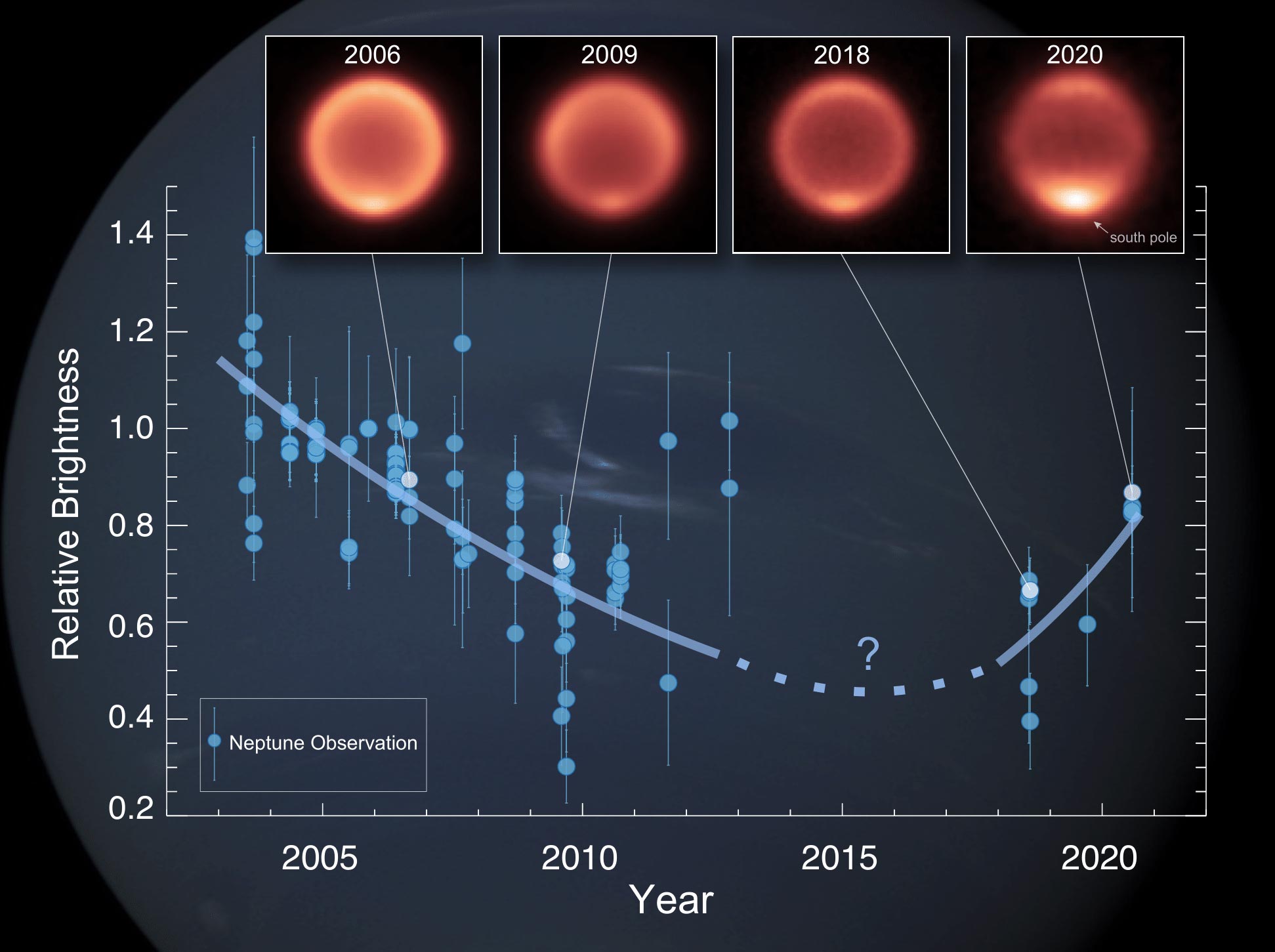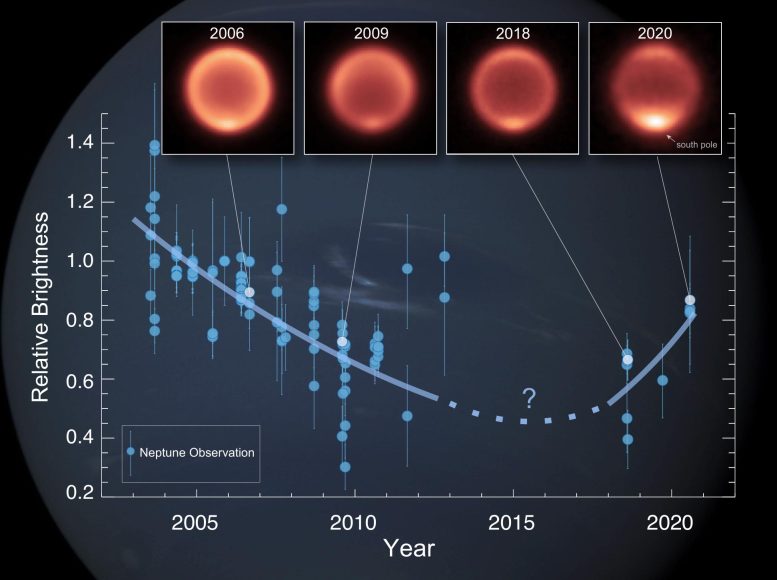
해왕성 대기의 온도 측정값인 해왕성의 열적외선 밝기의 변화를 관찰했습니다. 플롯은 지상 망원경으로 촬영한 기존의 모든 이미지에 대해 시간 경과에 따른 해왕성 성층권의 열적외선 밝기의 상대적 변화를 보여줍니다. 밝은 이미지는 따뜻한 것으로 해석됩니다. 약 12μm의 파장에서 해당 적외선 열화상(상단)은 2006년, 2009년, 2018년(유럽 남방 천문대의 초대형 VISIR 기기로 관찰) 및 2020년(스바루의 COMICS 기기로 관찰)에 해왕성의 모습을 보여줍니다. 남극 대륙은 지난 몇 년 동안 상당히 따뜻해진 것으로 보입니다. 출처: Michael Roman/NASA/JPL/Voyager-ISS/Justin Cowart
해왕성은 우리가 생각했던 것보다 차갑다
레스터 대학의 천문학자들이 주도한 새로운 연구는 온도가 얼마나 높은지를 밝혀냈습니다.[{” attribute=””>Neptune’s atmosphere have unexpectedly fluctuated over the past two decades.
The study, published today (Monday, April 11, 2022) in Planetary Science Journal, used observations in thermal-infrared wavelengths beyond the visible light spectrum, effectively sensing heat emitted from the planet’s atmosphere.
An international team of researchers, including scientists from Leicester and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), combined all existing thermal infrared images of Neptune gathered from multiple observatories over almost two decades. These include the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope and Gemini South telescope in Chile, together with the Subaru Telescope, Keck Telescope, and the Gemini North telescope, all in Hawai’i, and spectra from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope.

Neptune as seen in visible light (centre) and thermal-infrared wavelengths (right), in 2020. The centre image combines multiple images from the Hubble Space Telescope, while the thermal-infrared image on the right was taken from the Subaru Telescope on Maunakea, Hawai’i. In the thermal-infrared, Neptune’s warm south pole glows more brightly than ever seen before. Credit: Michael Roman/NASA/ESA/STSci/M.H. Wong/L.A. Sromovsky/P.M. Fry
By analyzing the data, the researchers were able to reveal a more complete picture of trends in Neptune’s temperatures than ever before.
But to the researchers’ surprise, these collective datasets show a decline in Neptune’s thermal brightness since reliable thermal imaging began in 2003, indicating that globally-averaged temperatures in Neptune’s stratosphere – the layer of the atmosphere just above its active weather layer – have dropped by roughly 8 degrees Celsius (14 degrees Fahrenheit) between 2003 and 2018.
Dr. Michael Roman, Postdoctoral Research Associate at the University of Leicester and lead author on the paper, said:
“This change was unexpected. Since we have been observing Neptune during its early southern summer, we would expect temperatures to be slowly growing warmer, not colder.”
Neptune has an axial tilt, and so it experiences seasons, just like Earth. However, given its great distance from the Sun, Neptune takes over 165 years to complete an orbit around its host star, and so its seasons change slowly, lasting over 40 Earth-years each.
Dr. Glenn Orton, Senior Research Scientist at JPL and co-author on the study, noted:
“Our data cover less than half of a Neptune season, so no one was expecting to see large and rapid changes.”
Yet, at Neptune’s south pole, the data reveal a different and surprisingly dramatic change. A combination of observations from Gemini North in 2019 and Subaru in 2020 reveal that Neptune’s polar stratosphere warmed by roughly 11°C (~20°F) between 2018 and 2020, reversing the previous globally-averaged cooling trend. Such polar warming has never been observed on Neptune before.
The cause of these unexpected stratospheric temperature changes is currently unknown, and the results challenge scientists’ understanding of Neptune’s atmospheric variability.
Dr. Roman continued:
“Temperature variations may be related to seasonal changes in Neptune’s atmospheric chemistry, which can alter how effectively the atmosphere cools.
“But random variability in weather patterns or even a response to the 11-year solar activity cycle may also have an effect.”
The 11-year solar cycle (marked by periodic variation in the Sun’s activity and sunspots) has been previously suggested to affect Neptune’s visible brightness, and the new study reveals a possible, but tentative, correlation between the solar activity, stratospheric temperatures, and the number of bright clouds seen on Neptune.
Follow-up observations of the temperature and cloud patterns are needed to further assess any possible connection in the years ahead.
Answers to these mysteries and more will come from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), which is set to observe both ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, later this year.
Leigh Fletcher, Professor of Planetary Science at the University of Leicester, will lead such observations with allocated time of JWST’s suite of instruments. Professor Fletcher, also a co-author on this study, said:
“The exquisite sensitivity of the space telescope’s mid-infrared instrument, MIRI, will provide unprecedented new maps of the chemistry and temperatures in Neptune’s atmosphere, helping to better identify the nature of these recent changes.”
Reference: “Sub-Seasonal Variation in Neptune’s Mid-Infrared Emission” 11 April 2022, Planetary Science Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/PSJ/ac5aa4
This study was funded by a European Research Council grant to the University of Leicester, known as GIANTCLIMES. This project has previously discovered long-term changes in atmospheric temperatures and clouds on the gas giants, Jupiter and Saturn, and it provided the first maps of the stratospheric temperatures of Uranus. GIANTCLIMES has paved the way for new discoveries on all four giant planets from JWST in the years to come.
Additional co-authors on this work include Thomas Greathouse (Southwest Research Institute), Julianne Moses (Space Science Institute), Naomi Rowe-Gurney (Howard University / NASA Goddard Space Flight Center), Patrick Irwin (Oxford), Arrate Antuñano (UPV/EHU), James Sinclair (JPL), Yasumasa Kasaba (Tohoku University), Takuya Fujiyoshi (Subaru Telescope), Imke de Pater (UC Berkeley), and Heidi Hammel (Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy).

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”