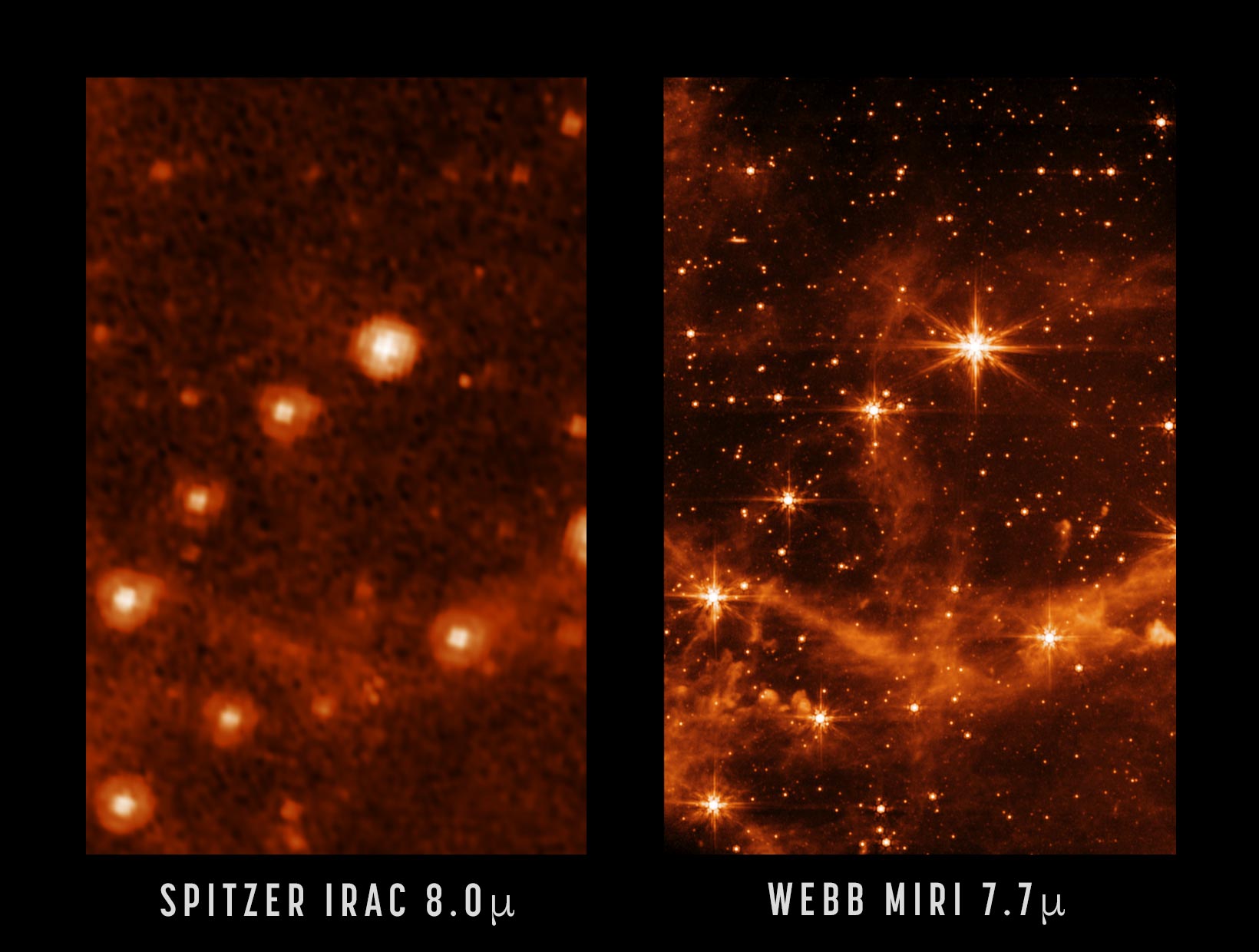
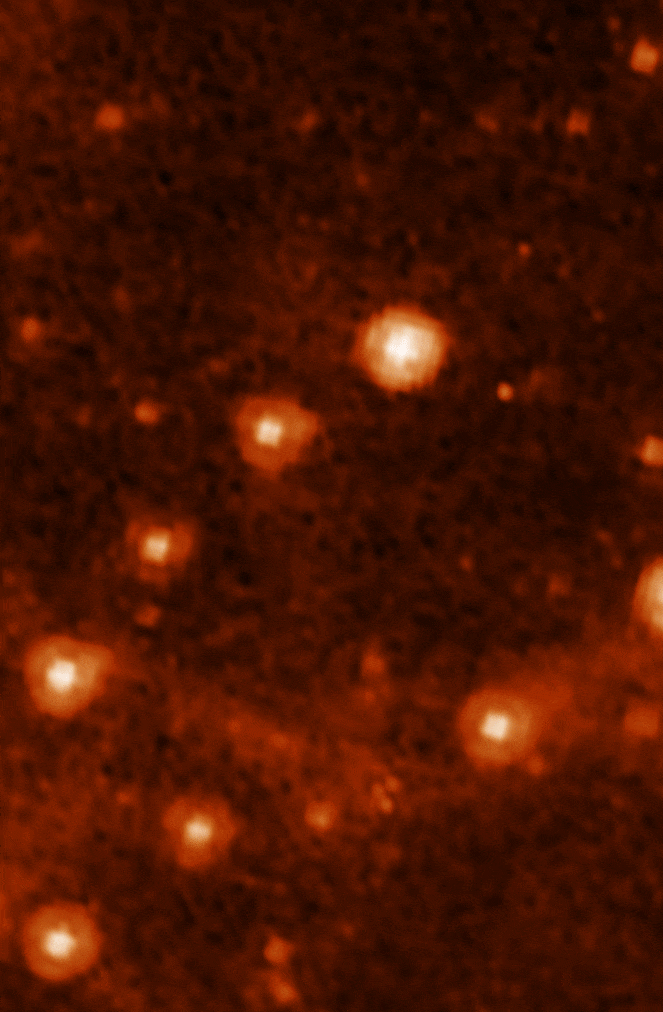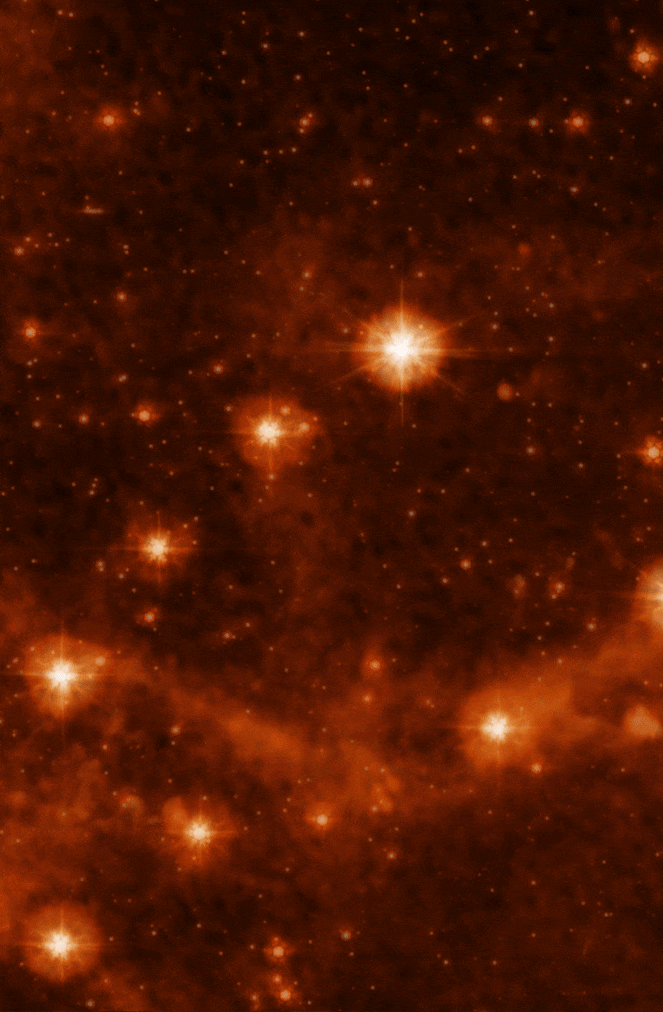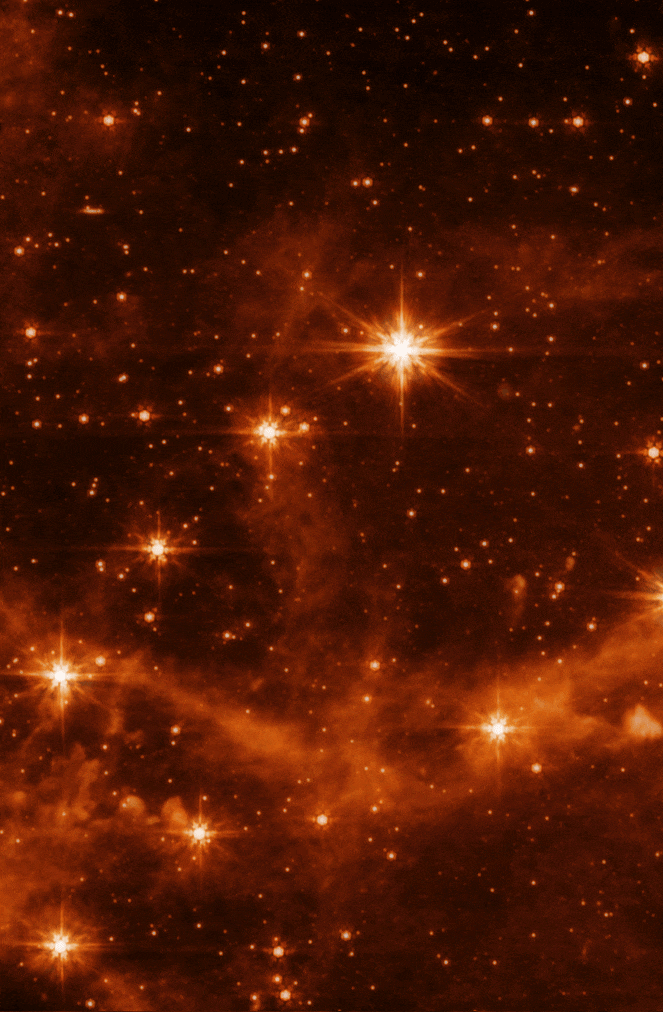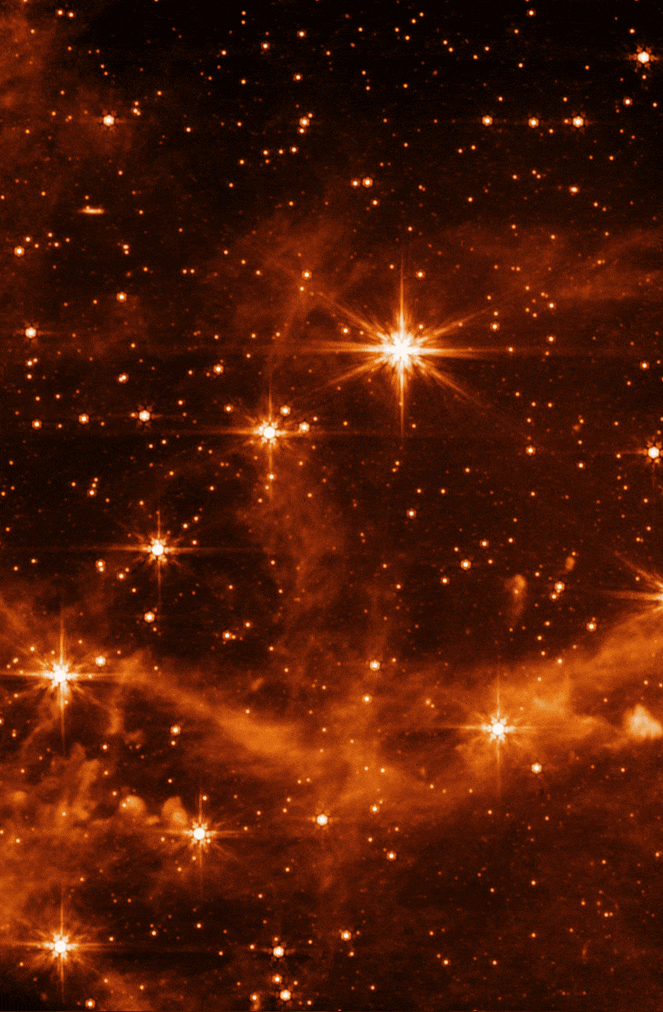
Webb 우주 망원경과 대마젤란 성운의 중적외선 기기 이미지와 Spitzer 우주 망원경의 적외선 배열 카메라를 사용한 동일한 장면의 이전 이미지 비교. 출처: NASA/JPL-Caltech(왼쪽), NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI(오른쪽)
James Webb Space Telescope is aligned across all four of its science instruments, as seen in a previous engineering image showing the observatory’s full field of view. Now, we take a closer look at that same image, focusing on Webb’s coldest instrument: the Mid-Infrared Instrument, or MIRI.
The MIRI test image (at 7.7 microns) shows part of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). This small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, located about 160,000 light-years away, provided a dense star field to test Webb’s performance.
Here, a close-up of the MIRI image is compared to a past image of the same target taken with NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope’s Infrared Array Camera (at 8.0 microns). The retired Spitzer telescope was one of NASA’s Great Observatories and the first to provide high-resolution images of the near- and mid-infrared universe. Webb, with its significantly larger primary mirror and improved detectors, will allow us to see the infrared sky with improved clarity, enabling even more discoveries.

Comparison of a Webb MIRI image of the Large Magellanic Cloud and a past image of the same view using the Spitzer IRAC. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech (top), NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI (bottom)
For example, Webb’s MIRI image shows the interstellar gas in unprecedented detail. Here, you can see the emission from “polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons,” or molecules of carbon and hydrogen that play an important role in the thermal balance and chemistry of interstellar gas. When Webb is ready to begin science observations, studies such as these with MIRI will help give astronomers new insights into the birth of stars and protoplanetary systems.
In the meantime, the Webb team has begun the process of setting up and testing Webb’s instruments to begin science observations this summer.
The James Webb Space Telescope is an international partnership between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). MIRI is part of Europe’s contribution to the Webb mission. It is a partnership between Europe and the USA; the main partners are ESA, a consortium of nationally funded European institutes, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC).

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”