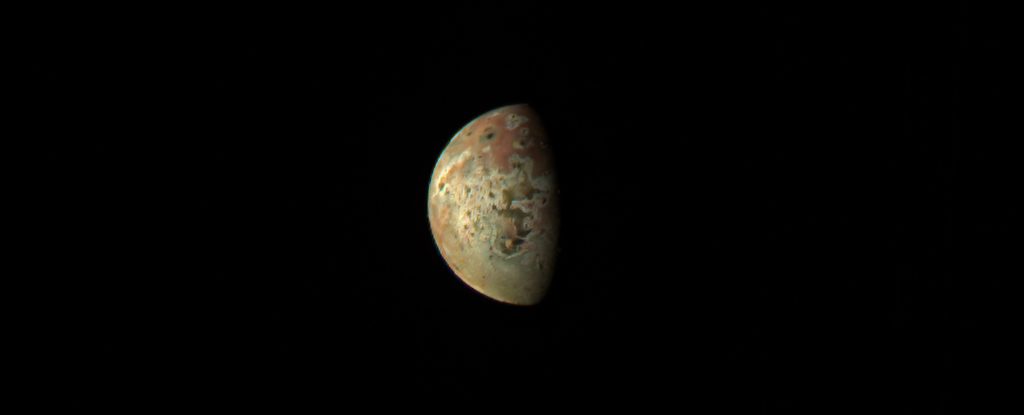
When the universe was emerging a billion years old, a galaxy A gigantic and fast-moving jet of radiation and plasma spewed out into the universe. After nearly 13 billion years, that plane became visible to humans in the form of a laser. The plane was photographed recently And analyzed by a team of Italian astronomers. Their findings, which give a sense of the plane’s length and speed, were recently published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
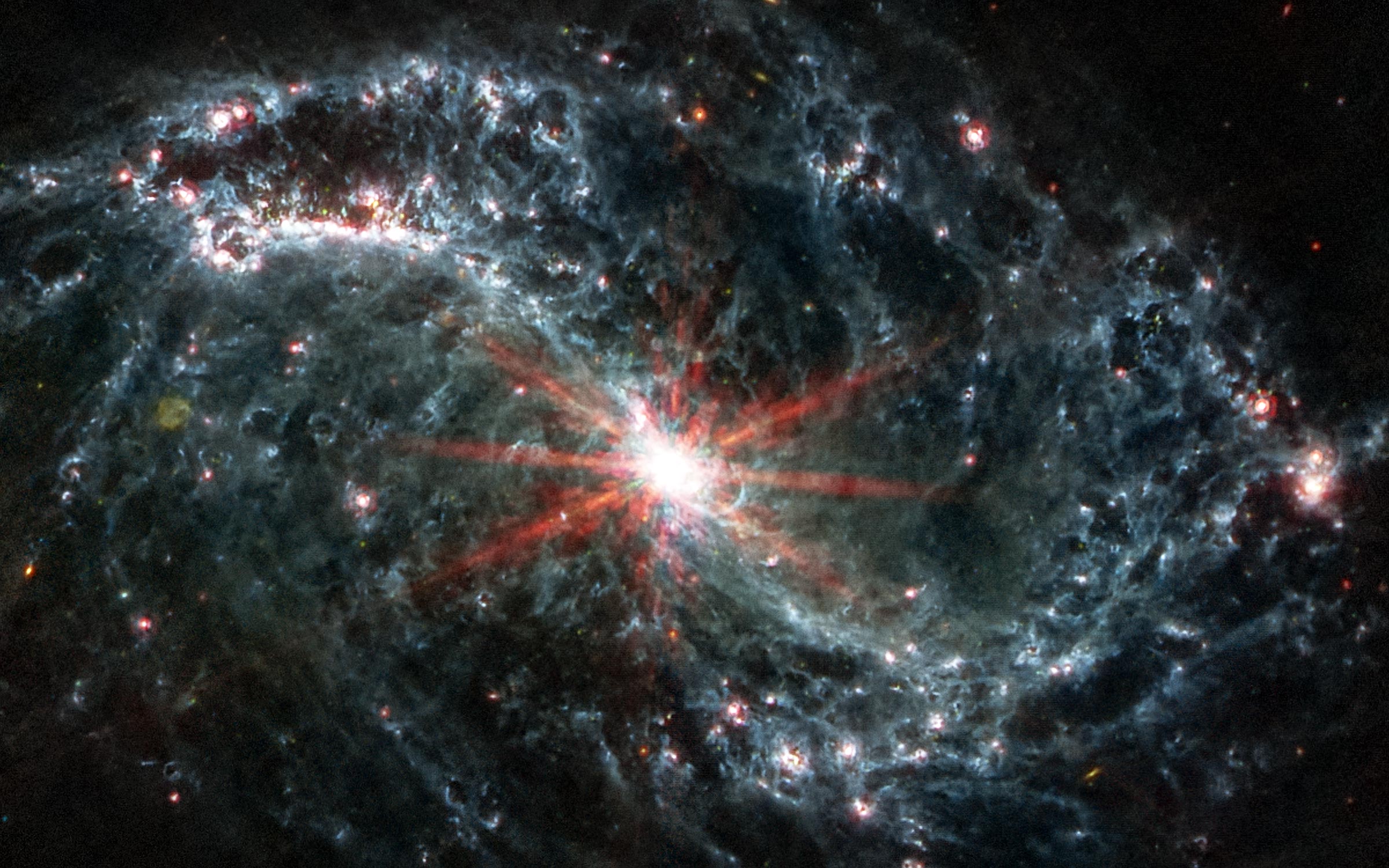
Seen through Very long base array– A formation of 10 radio telescopic antennas extending from St. What was actually captured in the false-color image, though, is a flux of bright orange plasma, oriented roughly toward us and spanning about 1,600 light-years, a distance that defies any terrestrial analogy.
According to Christiana Spingola, astronomer at the University of Bologna and lead author of the latest research paper, scientists are not seeing as many blazars as would be expected in the early universe.
“Among the various scenarios, this mismatch may be due to distant blazars that have different characteristics as locals, such as that the plane is moving slower than it does locally,” Spingola wrote in an email. “This is what our results suggest. If confirmed, we will find that local and remote blazars are different monsters.”
These jets are emitted from the centers of galaxies by supermassive black holes. Black holes accumulate disks of matter around them, sometimes spewing jets of material outward at an unusual speed. These galactic centers, called active galactic cores, are known as quasars. When the beams they throw off are directed at us, they are called plasars.
G / O Media may receive a commission
Two years ago, Blazars Have been found Sources of high-energy cosmic rays, converting them from an interesting topic into a compelling source of information about the early universe. First discovered in March 2020, the newly described star, called PSO J030947.49 + 271757.31 (short for PSO J0309 + 27), is located in the constellation Aries, about 12.8 billion light-years from Earth. The blazar is the brightest in radio waves and the second brightest in x-rays among those less than a billion years old. It’s also the farthest galaxy we’ve seen spewing out such a jet, making it also the oldest blazar ever observed.
These properties make it an ideal object to study [active galactic nuclei] At cosmic distances, “Spingola wrote.” We know very little about the young universe, so any new information is necessary to better understand that era. “
The team found that the Blazer plane was moving at three quarters of the speed of light. At an extraordinary rate, albeit not the fastest, other blazers were recorded at more than 90% of the speed of light.
The nice streak you see is actually an image made by combining three different observations of the plane, captured at different radio frequencies, to create invisible structures for the other plane. Finally, the image shows the blazer plane extending upwards into the blank black, with the brightest part downward, where the star’s core is located.

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”