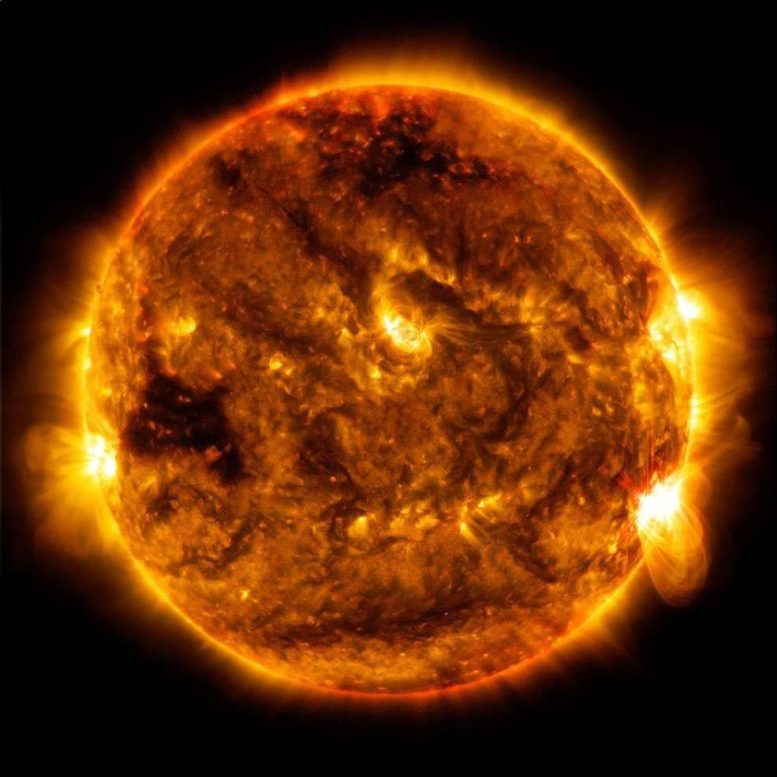
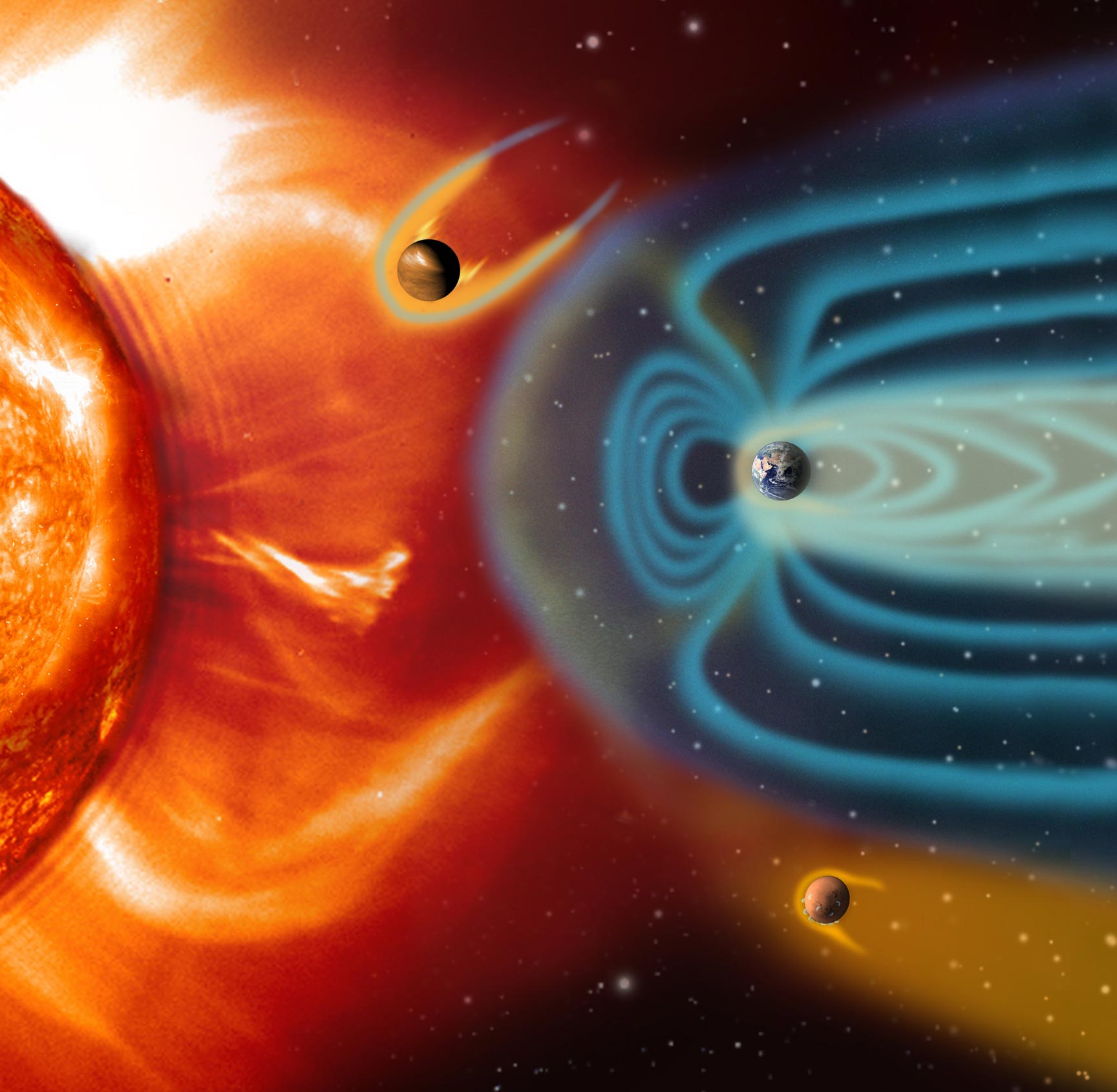
NASA의 Solar Dynamics Observatory가 포착한 2015년 10월 1일 오후 8시 13분(EDT)에 정점에 도달한 중간 수준의 태양 플레어. 크레딧: NASA/SDO
MUSE) and HelioSwarm – to help improve our understanding of the dynamics of the Sun, the Sun-Earth connection, and the constantly changing space environment. These missions will provide deeper insights into our universe and offer critical information to help protect astronauts, satellites, and communications signals such as GPS.
“MUSE and HelioSwarm will provide new and deeper insight into the solar atmosphere and space weather,” said Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for science at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “These missions not only extend the science of our other heliophysics missions—they also provide a unique perspective and a novel approach to understanding the mysteries of our star.”
MUSE
The MUSE mission will help scientists understand the forces driving the heating of the Sun’s corona and the eruptions in that outermost region that are at the foundation of space weather. The mission will offer deeper insight into the physics of the solar atmosphere by using a powerful instrument known as a multi-slit spectrometer to observe the Sun’s extreme ultraviolet radiation and obtain the highest resolution images ever captured of the solar transition region and the corona.
The mission will also provide complementary observations from heliophysics research such as the Extreme UltraViolet Spectroscopic Telescope and ground-based observatories.
“MUSE will help us fill crucial gaps in knowledge pertaining to the Sun-Earth connection,” said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters. “It will provide more insight into space weather and complements a host of other missions within the heliophysics mission fleet.”
The primary goal of the MUSE mission is to investigate the causes of coronal heating and instability, such as flares and coronal mass ejections, and gain insight into the basic plasma properties of the corona. MUSE will obtain high-resolution images of the evolution of solar flare ribbons in a field of view focused on a large, active region on the Sun.
The principal investigator for the MUSE mission is Bart DePontieu of the Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center (LMATC) of Palo Alto, California. This mission has a budget of $192 million. LMATC will provide project management.
HelioSwarm
The HelioSwarm mission is a constellation or “swarm” of nine spacecraft that will capture the first multiscale in-space measurements of fluctuations in the magnetic field and motions of the solar wind known as solar wind turbulence. The Sun’s outermost atmospheric layer, the heliosphere, encompasses an enormous region of the solar system. Solar winds spread through the heliosphere, and their interactions with planetary magnetospheres and disruptions such as coronal mass ejections affect their turbulence.
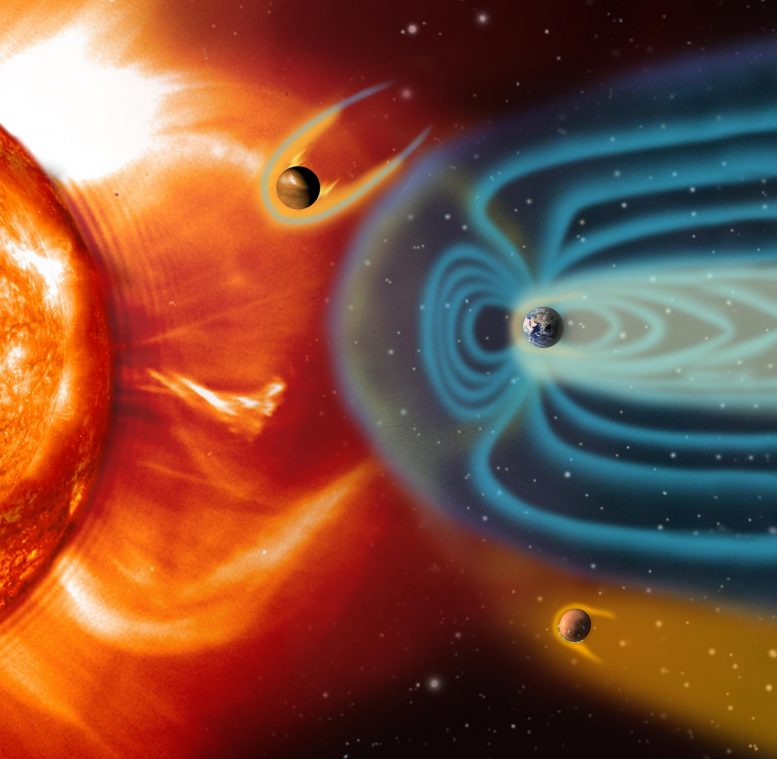
Artist impression (not to scale) illustrates how the solar wind shapes the magnetospheres of Venus (top), Earth (middle), and Mars (bottom). Credit: ESA
Studying solar wind turbulence across large areas requires plasma measurements taken simultaneously from different points in space. HelioSwarm consists of one hub spacecraft and eight co-orbiting small satellites that range in distance from each other and the hub spacecraft. The hub spacecraft will maintain radio contact with each small satellite. All radio contact between the swarm and Earth will be conducted through the hub spacecraft and the NASA Deep Space Network of spacecraft communication antennas.
“The technical innovation of HelioSwarm’s small satellites operating together as a constellation provides the unique ability to investigate turbulence and its evolution in the solar wind,” said Peg Luce, deputy director of the Heliophysics Division.
The HelioSwarm mission’s principal investigator is Harlan Spence from the University of New Hampshire. The mission’s budget is $250 million. NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California, will provide project management.
Funding and management oversight for these missions is provided by the Heliophysics Explorers Program, managed by the Explorers Program Office at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”